
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, Collaborative Innovation Center for Optoelectronic Semiconductors and Efficient Devices, Jiujiang Research Institute, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 e-mail: gysun@xmu.edu.cn
3 e-mail: zlyang@xmu.edu.cn
The light manipulation beyond the diffraction limit plays an invaluable role in modern physics and nanophotonics. In this work, we have demonstrated a strong coupling with a large Rabi splitting of 151 meV between bulk excitons and anapole modes in the -Si nanodisk heterostructure array with nanoholes as small as 50 nm radius. This result is acquired by introducing anapole modes to suppress radiative losses to confine light into subwavelength volumes and large spatial overlapping between excitons and strong optical fields. Our work shows that anapole modes may serve as a powerful way to enhance the interaction between light and matter at nanoscales, and it should pave an avenue toward high-performance all-dielectric optoelectronic applications.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(7): 1744
中国民航大学电子信息与自动化学院, 天津 300300
针对基于三维(3D)变形模型的人脸图像重建方法对人脸特征点检测不准确导致的重构模型形状表达能力不稳健问题,提出了一种优化3D变形模型参数的重建方法。首先,通过改进的位置映射图网络准确提取和定位人脸特征点,并以此为基础得到初始模型参数。然后,为了提高模型的精准度和泛化能力,融合基于回归方法得到的参数获取优化的模型参数。最后,对3D变形模型进行优化,得到最终的人脸模型。用真实人脸作为实验数据的结果表明,本方法能实现精确的3D人脸重建。
机器视觉 三维人脸重建 三维变形模型 人脸特征点 模型参数 激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(20): 2015008
中国民航大学电子信息与自动化学院, 天津 300300
为了克服面部表情变化导致的三维人脸识别精度不高的问题,提出了一种结合局部关键点集与测地线的三维人脸识别算法。首先,根据表情变化对人脸识别具有分区域影响的特性,将三维人脸划分出刚性区域和非刚性区域;然后将由鼻部和眼部组成的区域作为刚性区域,进行有效关键点检测,提取多种几何特征,构成局部描述子,进行相似度匹配;接着在非刚性区域提取测地线环带并进行相似度匹配;最后将两个区域的匹配程度进行加权融合,得到最终的匹配结果。该算法分别在Bosphorus和FRGC v2.0数据库上进行了实验验证,结果表明算法识别率分别达到了97.01%和98.63%,由此证明本文算法对三维人脸的表情变化有较强的稳健性。
机器视觉 三维人脸识别 表情变化 关键点 局部描述子 测地线 激光与光电子学进展
2020, 57(22): 221503
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, Collaborative Innovation Center for Optoelectronic Semiconductors and Efficient Devices, Jiujiang Research Institute, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 Institute of Electromagnetics and Acoustics, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
3 College of Physics Science and Technology, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China
4 The First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University, Xiamen 361003, China
5 e-mail: nanoantenna@hotmail.com
6 e-mail: zlyang@xmu.edu.cn
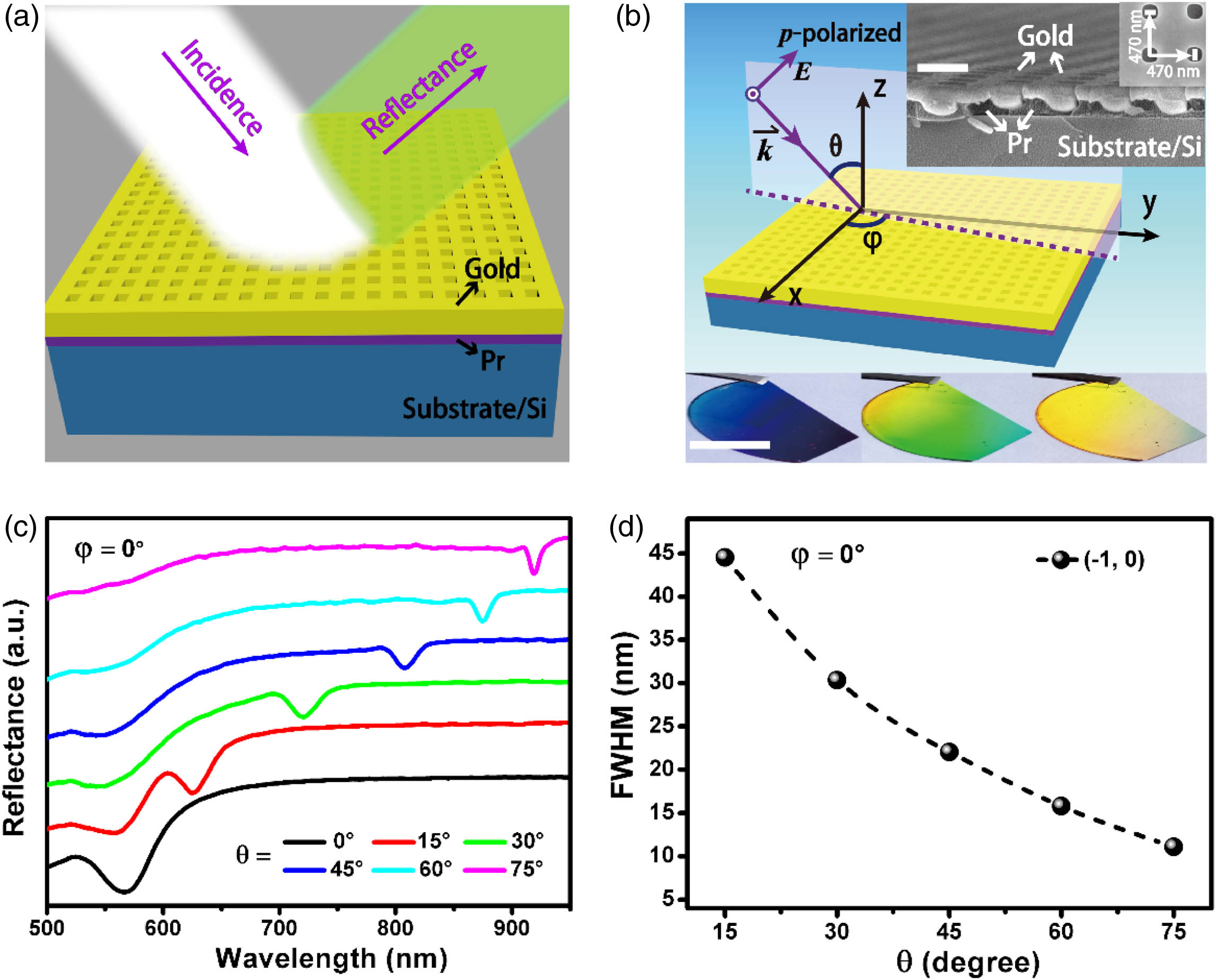
Coupling effects of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) induce changes in the wavelength, intensity, and linewidth of plasmonic modes. Here, inspired by coupling effects, we reveal an abrupt linewidth-shrinking effect in 2D gold nanohole arrays at the azimuthal angle of 45° arising from the interference of two degenerate SPR modes. We further demonstrate the biosensing capability under various excitation conditions for detecting the critical molecular biomarker of prostatic carcinoma, and achieve the maximum sensitivity at this angle. Our study not only enhances the understanding toward plasmonic resonance-linewidth shrinking, but also provides a promising strategy to greatly improve biosensing performance by light manipulation on plasmonic nanostructures.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(7): 07001226
1 北京化工大学机电工程学院, 北京 100029
2 北京化工大学理学院, 北京 100029
提出了一种能够实现近红外区域(780~1100 nm)高反射的聚合物交替多层聚碳酸酯(PC)/聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯(PMMA) 周期性光学薄膜的设计方案,验证了利用微纳层叠共挤设备制备特殊多层光学膜结构的可行性。利用遗传算法搜索出4个周期的最优布拉格中心波长,得出了最优膜的总厚度。仿真了4个周期叠加多层膜的光谱特性,讨论了入射角及厚度误差对多层膜近红外区域总反射率的影响。研究结果表明,所提方案满足对太阳光的隔热及内部智能采光的需求。
薄膜 近红外区域 高反射 聚碳酸酯/聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯 微层共挤 遗传算法 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(4): 041601





